An Objective Look At Google News: Is It Really Biased?
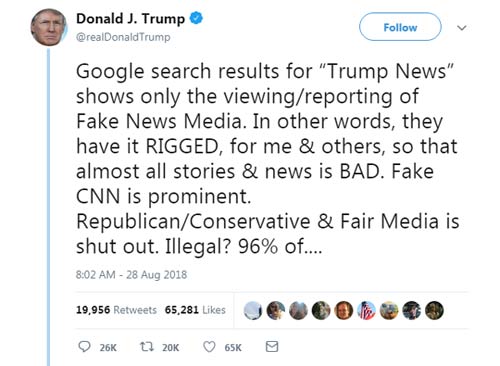
Recent revelations have shown that the United States Government is looking into regulating Google search results in response to publicly tweeted claims from Donald Trump.
In them, he stated that search results were displaying articles that were biased against him. In particular, he highlighted results showing within Google News:
Roger Montti has done a great job of summarising the initial resistance from the SEO community in his post, and as he points out — Google’s Page Ranks are entitled to First Amendment protection.
Roger also touched on whether or not Google can be biased, and as algorithms are programmed by humans, the answer in short is that they can. However as we know, Google News works differently to regular Google search.
So, to understand whether or not this feature can be biased, we first need to look at how Google News works and how it visually impacts search results for users.
Google News
Google News is a separate vertical within Google Search, focusing on recent news stories and articles. The pages that Google News uses come from a manually curated index, to which sites have to apply to be included.
There are several requirements for sites to be considered for Google News — some technical, some editorial — and Google is quite strict about the types of sites it allows in the index.
Websites that want to be included in Google News need to be focused primarily on news. A news section of an e-commerce site would not qualify. You also need to produce original content on a regular basis, ideally with multiple contributing authors.
Technically, you need to implement the right structured data on your articles, have a news-specific XML sitemap, and ensure your content can be easily indexed by Google. Implementing AMP versions of your articles is also highly recommended, as Top Stories on mobile are almost exclusively AMP.
The actual Google News vertical is not that big of a traffic source for news publishers. What drives most of the search traffic to news sites is the Top Stories carousel that appears in 10%-12% of regular Google organic search results. An appearance in Top Stories can drive thousands, or even millions, of views to an article, especially for topics that are very popular or current.
Top Stories
Top Stories is nearly entirely powered by Google News. While technically Top Stories is a feature of Google’s regular web search, over 99% of articles that appear in the Top Stories carousel come from sites that are included in Google News.
Also, we tend to see improved visibility in Top Stories that correlate with improved visibility in Google News, so we know that both search types take a lot of the same ranking factors in to account.
The algorithms that decide if an article should show up in Top Stories and/or Google News are focused on several different aspects:
- Is the article relevant for the search query?
- Is the article recently published or updated?
- Is it a unique article from an original publisher?
- Is the publisher known to write articles about that topic?
- Is the publisher trustworthy and of sufficient quality?
Some of these are under the direct control of the publisher; well-optimised title tags and headlines go a long way. However, even with the best optimised content you’re not guaranteed a spot in the Top Stories carousel — or anywhere in Google News for that matter. Google’s algorithms are the ultimate arbiters, and they look at a wide range of factors.
Determining Quality
How for example, does Google determine the quality of a news site?
- Does it have to do with the number of advertising slots on a page (which are the lifeblood of most news websites)?
- The originality and tone of voice of your articles?
- How many internal links do you have in any given article, and what is the relevancy of those links?
- Are there domain-wide quality metrics or is it on a page-by-page basis?
- Does the number of articles a news site publishes have an impact?
The quality factor is something that Google has been putting extra focus on since 2017, and news organisations have been trying to second-guess its inner workings. Quality can be hard to define, but more and more we see algorithmic interpretations of subjective human quality evaluations come in to play in Google’s ranking algorithms.
So What Results Does Google Show?
In order to assess this objectively, I’ve used a VPN to emulate Google.com (with an IP in Washington, DC), and have looked at a number of fairly generic search queries relating to “trump news” that have high search volumes (taken from Serpstat), including phrases such as “trump news” which has a search volume of 2,740,000 monthly, and “trump news today” which has a search volume of 368,000 monthly.
I’ve then performed these searches and logged the publications that appear for each query in the Top Stories SRCB. I then looked at the frequency in which each result appeared, and categorised its political allegiance using the Political bias lists from mediabiasfactcheck.com.
| News Source | Frequency | Political Bias |
| CNN | 24 | Left |
| Politico | 4 | Left-Centre |
| USA Today | 4 | Left-Centre |
| NBC | 3 | Left-Centre |
| HuffPost | 2 | Left |
| Washington Post | 2 | Left-Centre |
| Fox News | 2 | Right |
| ZDNet | 1 | Left-Centre |
| LA Times | 1 | Left-Centre |
| NPR | 1 | Left-Centre |
| Telegraph UK | 1 | Right-Centre |
| Boing Boing | 1 | Left |
| Economic Times | 1 | Left-Centre |
| CNBC | 1 | Left-Centre |
| Townhall | 1 | Right |
| The Independent | 1 | Left-Centre |
| The Week | 1 | Left-Centre |
| The Guardian | 1 | Left-Centre |
As you can see from the data, the results are heavily dominated by news publications deemed to be left-centre of the political spectrum.
Although there are indeed only two right wing publications in the list, we could surmise that Google simply finds that on average, people wish to view more left wing publications, or that they are simply better at fulfilling Google News’ criteria.